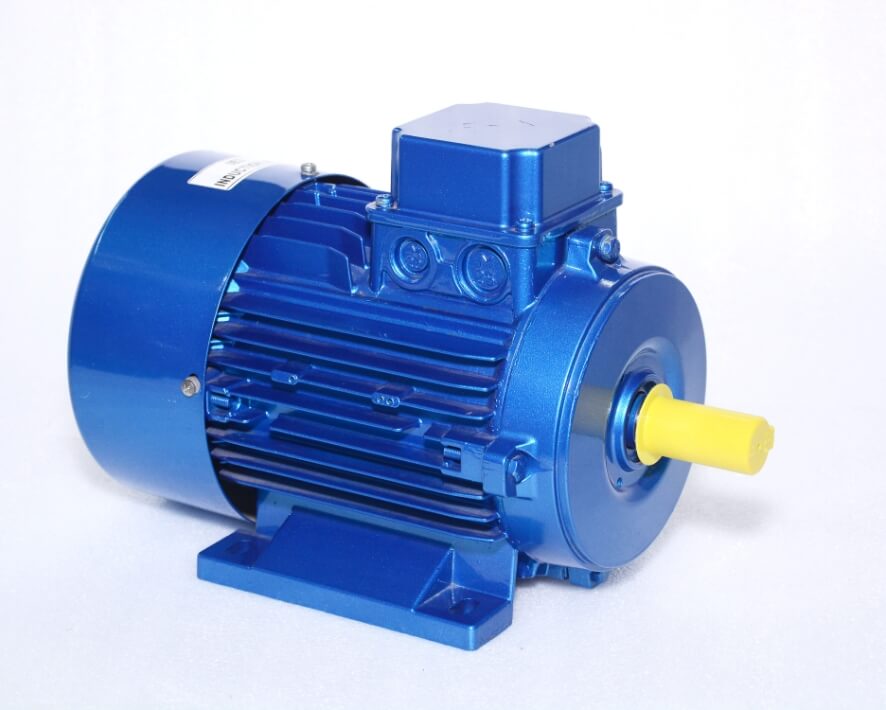
Induction Motor
An induction motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic induction
Quantities used in Induction motors
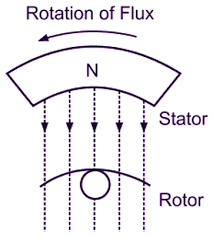
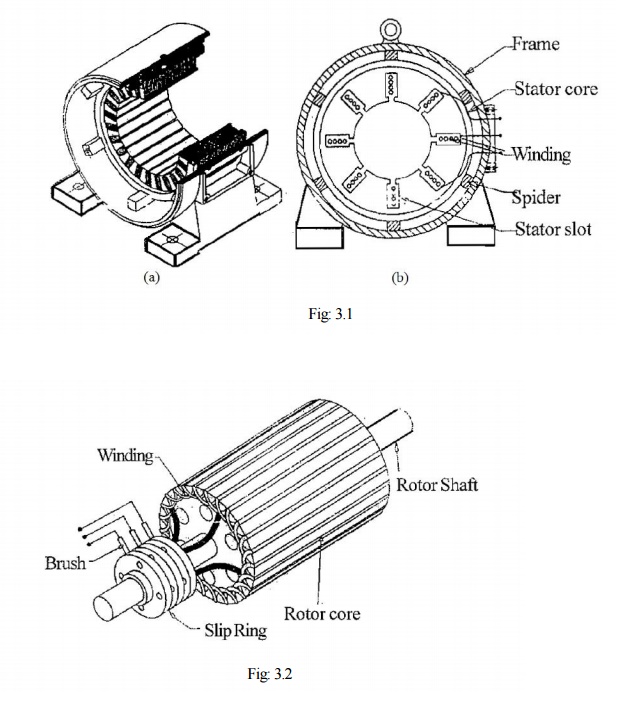
Stator:
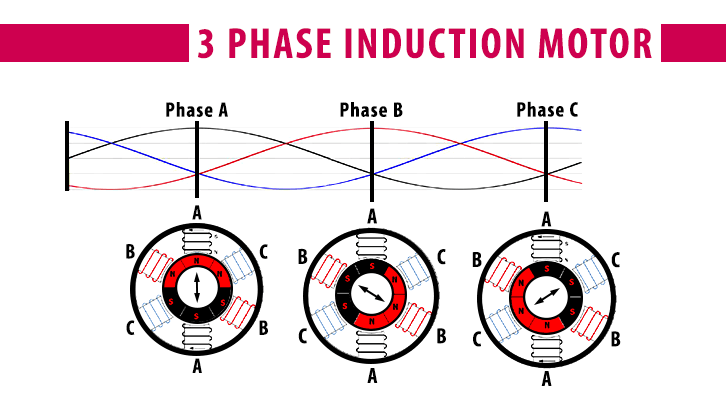
The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of three windings (phases) that produce a rotating magnetic field when supplied with 3-phase AC power.
Rotor:
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor that experiences the effects of the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator. It induces current and torque, causing the rotor to turn.
Stator Windings (U, V, W):
The stator windings are three sets of windings, typically labeled U, V, and W, which are energized by the 3-phase AC power supply to create a rotating magnetic field.
Rotor Bars and End Rings:
The rotor consists of bars that are short-circuited by end rings. As the rotor turns within the magnetic field, currents are induced in the rotor conductors, generating torque.
Slip (s):
Slip is a parameter that quantifies the difference between the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field and the actual rotor speed. It is expressed as a percentage and is crucial for understanding motor performance.
Synchronous Speed (N_sync):
Synchronous speed is the theoretical speed at which the magnetic field produced by the stator rotates. It is determined by the frequency of the power supply and the number of poles in the motor.
Rotor Speed (N):
The rotor speed is the actual speed at which the rotor of the motor turns. It is always less than the synchronous speed due to slip.
Torque (T):
Torque is the turning force produced by the motor. In a 3-phase induction motor, torque is generated due to the interaction between the magnetic field and the rotor currents.
Frequency (f):
Frequency represents the number of cycles per second in the 3-phase AC power supply. It affects the synchronous speed of the motor.
Power Factor (PF):
Power factor is the cosine of the angle between the voltage and current waveforms in the motor. It indicates the efficiency of power transfer from the supply to the motor.
Efficiency (η):
Efficiency is a measure of how effectively the motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. It is expressed as a percentage.
Locked Rotor Current (I_start):
The locked rotor current is the current drawn by the motor when the rotor is stationary. It is typically higher than the operating current and is important for motor protection considerations.
Innovative Practical Applications of 3-Phase Induction Motors
1. Used extensively in industrial machinery like pumps, fans, compressors, conveyors due to reliability and robustness.
2. Critical components in HVAC systems for efficient air circulation and temperature control.
3. Play vital role in water treatment plants, powering pumps and agitators.
4. Drive equipment like pumps and compressors in oil and gas industry.
5. Power heavy mining machinery such as crushers and conveyors.
6. Used in electric vehicles for propulsion.
7. Employed as generators in some wind turbines for renewable power generation.
8. Drive various machines involved in paper production process.
9. Used in agricultural equipment like irrigation pumps and grain handling systems.
10. Power the traction systems of electric trains in railway electrification.
These are just some of the many diverse applications of induction motors.
Indian-Specific Trivia on 3-Phase Induction Motors:
Agricultural Pumping Systems:
In India, 3-phase induction motors are extensively employed in agricultural pumping systems, playing a vital role in irrigation and supporting the country's agrarian economy.
Rural Electrification:
3-phase induction motors have been instrumental in rural electrification projects across India, bringing power to remote villages and contributing to agricultural mechanization.
Domestic Water Supply:
In urban and rural areas alike, 3-phase induction motors power water pumping stations for domestic water supply, ensuring a consistent and reliable distribution of water.
Textile Mills:
India has a rich tradition in the textile industry, and 3-phase induction motors are extensively used in textile mills for powering machinery involved in spinning, weaving, and processing.
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
Small and medium enterprises in India rely on 3-phase induction motors for various applications, including manufacturing processes, equipment operation, and overall industrial productivity.
Wastewater Treatment Plants:
3-phase induction motors are crucial in wastewater treatment plants across India, contributing to the efficient operation of pumps, mixers, and aeration systems in the treatment processes.
Mining Operations:
The mining sector in India extensively uses 3-phase induction motors to power equipment for excavation, material handling, and mineral processing, supporting the extraction of minerals.
Railway Electrification Projects:
India's ambitious railway electrification projects involve the use of 3-phase induction motors in electric trains, enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of the country's railway transportation.
Paper and Pulp Industry in India:
The Indian paper and pulp industry relies on 3-phase induction motors to drive machinery such as pulpers, refiners, and paper machines, contributing to the production of paper and related products.
Renewable Energy Generation:
In India's pursuit of renewable energy, 3-phase induction generators are utilized in some wind turbines to harness wind power for electricity generation in regions with favorable wind conditions.
Agro-Processing Units:
Agro-processing units in India, involved in activities like rice milling, oilseed processing, and sugar refining, utilize 3-phase induction motors to power machinery for food processing and value addition.
Automotive Manufacturing:
The automotive manufacturing industry in India relies on 3-phase induction motors for various applications, including conveyor systems, robotic assembly lines, and equipment used in vehicle production.
Understanding the widespread applications of 3-phase induction motors in the Indian context highlights their integral role in driving economic activities, infrastructure development, and improving the quality of life across different sectors of the country. As India continues to grow and modernize, the demand for efficient and reliable motor systems remains essential for sustainable development.