TRANSFORMERS
Transformers are electrical devices that transfer energy between circuits using electromagnetic induction. They operate based on Faraday's law which states that a changing magnetic field within a coil induces an EMF.

Some Important Quantities
1. Turns Ratio (N1/N2):
The turns ratio is the ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding (N1) to the number of turns in the secondary winding (N2). It determines the voltage transformation ratio of the transformer (V1/V2 = N1/N2).
2. Voltage Rating (V1 and V2):
V1 and V2 represent the voltage ratings of the primary and secondary windings, respectively. The voltage transformation is based on the turns ratio, following the equation V1/V2 = N1/N2.
3. Current Rating (I1 and I2):
I1 and I2 represent the current ratings of the primary and secondary windings, respectively. The relationship between primary and secondary currents is inversely proportional to the turns ratio (I1/I2 = N2/N1).
4. Power Rating (S):
The power rating of a transformer, often denoted as S, is the product of voltage and current on either side (S1 = V1 * I1 = S2 = V2 * I2). It represents the maximum apparent power that the transformer can handle.
5. Core Losses (Iron Losses):
Core losses, also known as iron losses, occur due to hysteresis and eddy current losses in the transformer core. These losses are present even when there is no load on the transformer.
6. Copper Losses (I^2R Losses):
Copper losses, also known as I^2R losses, occur in the transformer windings due to the resistance of the conductors. These losses increase with the square of the current.
What are the different types of tranformers?
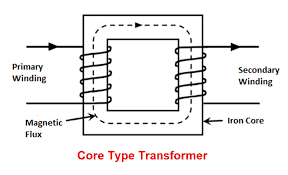
TYPE-1
Explore Start Free
- The core surround the windings.
- Typically have a circular or elliptical core cross-section, resulting in a longer magnetic path
- Both primary and secondary windings are usually wound on a single limb
- Slightly reduced cooling efficiency due to the longer magnetic path.
- Often preferred for high-voltage and large power applications.
TYPE-2
Explore Start Free
- The windings surrounds the core
- Often have a rectangular or square core cross-section, providing a shorter magnetic path
- Windings are distributed on both limbs of the core
- Offer better cooling due to the shorter magnetic path.
- Commonly used for distribution and small power transformers.

shell type transformer
Block Of Ui Kit Collections
Indian-Specific Trivia on Single-Phase Transformers:
Voltage Fluctuations:
In India, where voltage fluctuations are common in the electrical grid, single-phase transformers play a crucial role in stabilizing and providing a consistent voltage supply for residential and commercial use.
Rural Electrification:
Single-phase transformers have been integral to rural electrification initiatives in India, stepping down high-voltage power to levels suitable for distribution in remote and rural areas.
Power Grid Diversification:
In the diverse Indian power grid, single-phase transformers are employed in a range of applications, from urban centers with high power demands to rural regions with distributed power needs.
Voltage Stabilization in Urban Areas:
In densely populated urban areas, single-phase transformers are used in voltage stabilization units to protect electronic equipment and appliances from damage due to frequent voltage fluctuations.
Standby Power Systems:
Single-phase transformers are commonly used in standby power systems, providing a reliable and stable power source during outages, which is essential in regions with intermittent power supply.
Community Power Supply:
In certain community-driven power supply models, small-scale single-phase transformers are employed to distribute power locally, catering to the specific energy needs of small communities or villages.
Power Conditioning in Industries:
Industries in India often use single-phase transformers for power conditioning, helping to regulate voltage and ensure the stable operation of machinery and equipment in manufacturing units.
Voltage Regulation for Agricultural Applications:
Single-phase transformers are utilized in voltage regulation systems for agricultural applications, supporting irrigation systems and farm equipment in regions with variable power quality.
Transformer Manufacturing Industry:
India has a vibrant transformer manufacturing industry, producing a variety of single-phase transformers for both domestic and international markets. These transformers cater to diverse applications and voltage requirements.
Railway Electrification Projects:
In the ongoing railway electrification projects across India, single-phase transformers are used to adapt power from the grid to the specific voltage requirements of railway traction systems for electric trains.
Renewable Energy Integration:
Single-phase transformers play a role in integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the Indian electrical grid. They facilitate the transformation and distribution of power from these sources.
Emergency Power Systems in Urban Centers:
In urban centers prone to power outages, single-phase transformers are components of emergency power systems, providing backup power for critical infrastructure, businesses, and residential areas.
Understanding the specific applications of single-phase transformers in the Indian context highlights their critical role in addressing the diverse and dynamic energy landscape of the country.
As India continues to expand its electrical infrastructure, the importance of single-phase transformers in ensuring reliable and stable power supply remains significant.
Transformer Evaluation and Enhancement
At ElectroCalc Hub, we offer transformer property evaluation services which are easy to use, but highly functional. You can evaluate important parameters of your device such as efficiency, output voltage and many more.
